What Is Ancient Roman Art What Is Middle Ages Art
Just every bit Greece is known as the "cradle" or "birthplace" of our Western world or civilization, in almost equal regard, Rome is known as the "Capital of the World", otherwise Caput Mundi in Latin. Rome is the capital of Italy and the region of Lazio (as well known as Latium). Roman artwork is as various as Roman civilisation, ranging from paintings, sculpture, compages, mosaics, glasswork, metalwork, among many others. This article will explore the characteristics of Roman Art and simply how this once minor Italian settlement grew into the Head Mundi.
Table of Contents
- one The Eternal City: A Cursory Look at Roman History
- 1.ane The Etruscans (900 BC – 27 BC)
- 1.ii The Roman Kingdom (753 BC – 509 BC)
- 1.3 The Roman Republic (509 BC – 27 BC)
- 1.four The Roman Empire (27 BC – 476 BC)
- 2 Roman Artwork
- two.1 Roman Paintings
- 2.2 Roman Architecture
- 2.3 Roman Sculpture
- 3 The Weakened West Remains Eternal
- 4 Frequently Asked Questions
- 4.1 What Is Roman Art?
- 4.ii What Are the Characteristics of Roman Art?
- iv.3 What Are the 4 Styles of Roman Painting?
- 4.4 What Was the Difference Between Greek and Roman Art?
- 4.five Did the Romans Invent Concrete?
The Eternal City: A Cursory Await at Roman History
It was the Roman poet Tibullus who described Rome every bit "The Eternal Metropolis" (Urbs Aeterna) during the onest Century BC. The sentiment behind this endearing term came from the steadfast belief in Rome as a city, and her adequacy to endure and survive whatsoever war or hardship.
We will discover this appellation in Tibullus's Elegies (2.5, 23-24), referencing the myth of how Rome was institute by ii twin brothers, Romulus and Remus: "Romulus aeternae nondum formaverat urbis moenia, consorti non habitanda Remo." (This is translated from Latin to "Romulus had not even so built the walls of the eternal city where his blood brother Remus was not to alive in partnership").
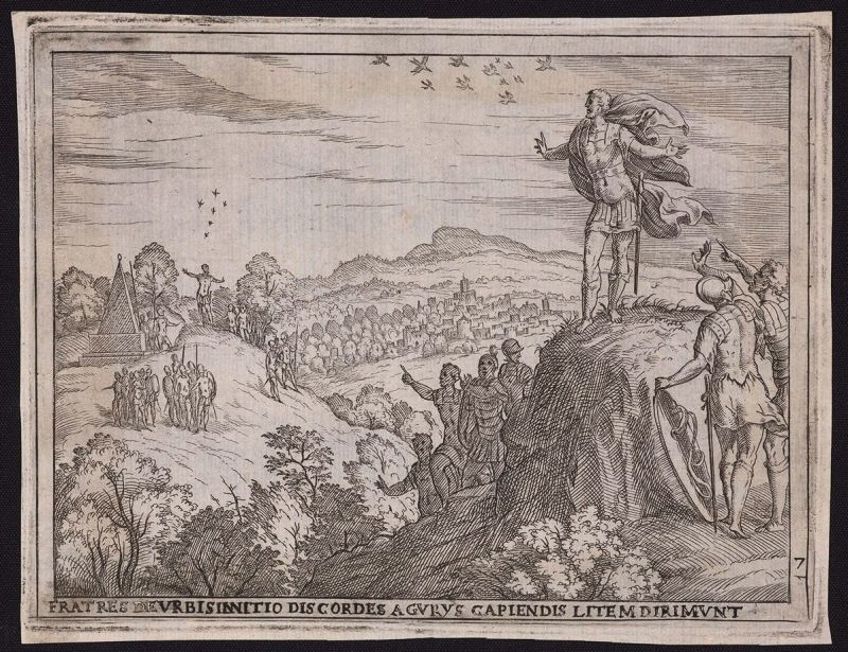 The Brothers, Disputing Over the Founding of Rome, Consult the Augurs, pl.7 from the series The Story of Romulus and Remus (1575) by Giovanni Battista Fontana;Giovanni Battista Fontana, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
The Brothers, Disputing Over the Founding of Rome, Consult the Augurs, pl.7 from the series The Story of Romulus and Remus (1575) by Giovanni Battista Fontana;Giovanni Battista Fontana, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
It was not but 1 poet who bolstered the city'south splendor, but others like Virgil, a now eternalized Roman poet, who wrote nigh Rome'due south inception in his Aeneid (29 BC-19 BC), an epic poem nigh the Trojan hero Aeneas and the founding of Rome. Rome is described past the god Jupiter as "imperium sine fine", which translates to "empire without end".
The founding of Rome and its proper noun is a widely debated topic, withal, one of the more popular origin stories or founding myths is of Romulus and Remus mentioned higher up (who are also believed to descend from Aeneas).
It was believed that the two brothers were orphaned and left for dead by the Tiber River by Amulius, their uncle and Rex of Alba Longa, who likewise took over the throne from his brother, Numitor. They were institute and nursed by a female person wolf and somewhen establish by Faustulus, a shepherd from the area, who gave them a dwelling house. When the twin brothers were adults, they learned most their history and murdered Amulius, re-enthroned Numitor, and set out to build a new city along the River Tiber.
However, historical myths indicate that Romulus murdered his brother and set out to build Rome himself. In that location are unlike reasons equally to why he killed his brother. Some are more common than others, for example, the two brothers disagreed about the location of the urban center along the River Tiber, which led to Romulus killing Remus.
When we think of Rome, we remember of the Colosseum, k architectural establishments, marble sculptures, including famous aboriginal Roman poets like Virgil or Ovid. Well-nigh Roman artwork is derived from the preceding Greek and Etruscan civilizations. Although there is so much more to the origins of Rome, below, we will have a brief look at the timeline of its development into a Head Mundi, so to say.
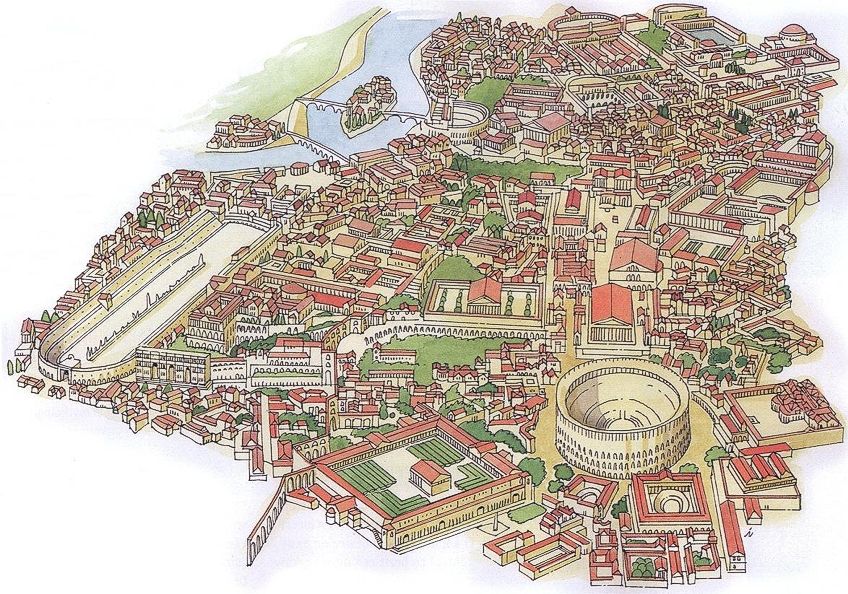 Model of what ancient Rome looked similar;Woeterman 94, CC BY-SA three.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Model of what ancient Rome looked similar;Woeterman 94, CC BY-SA three.0, via Wikimedia Commons
The Etruscans (900 BC – 27 BC)
Not much is left from the Etruscan culture, but what is known is that this civilisation initially started in prominent cities similar Florence and Pisa in Tuscany. The civilization'due south location was by and large around the Italian peninsula in Tuscany, Lazio, and Umbria. The Etruscans also traded with the Greeks, Egyptians, and Phoenicians, due to their locations around the Mediterranean.
The Villanovan culture (c. 900 BC–700 BC) is believed to take been the offset civilization right before the development of the Etruscan culture, which was eventually overtaken past Rome as it grew in power. Information technology is of import to identify Rome within context, as during this menstruum Rome was no more than a small settlement further s of the Italian Peninsula.
During 600 BC, Rome was overtaken past the Etruscan monarchy, partly because of the placement of the metropolis (Rome) on the River Tiber and the surrounding hills, which were ideal for defenses. The Etruscan kings ruling Rome were called the Tarquinii.
Rome was profoundly influenced past many cultural developments from Etruria and essentially, the Greeks.
Some of the more notable influences include the development of sewerage and drainage, agricultural irrigation, architectural designs, engineering science, building temples, gladiatorial games (which were originally a religious game for the Etruscans), as well as painting and sculpture.
The Roman Kingdom (753 BC – 509 BC)
While the Etruscans were absorbed by the Romans, Rome's form of government was a monarchy. The city had seven kings who ruled until Rome became a Republic. The first king was Romulus (reigning from 753-717 BC), the founder, and the second was Numa Pompilius (reigning from 716-673 BC), who reigned during a peaceful period in Rome's development and congenital various religious establishments, such as a temple dedicated to the Roman god Janus.
Tullus Hostilius (reigning from 673-642 BC) was the third male monarch. He was more aggressive in his reign and took over the city of Alba Longa. The fourth king was Ancus Marcius (reigning from 640-616 BC), the grandson to Numa. He re-established certain religious orders and won the war against the Latins and Sabines.
The fifth rex was Lucius Tarquinius Priscus (reigning from 616-579 BC), who was also the first Etruscan male monarch. He invaded and overpowered the Etruscan tribes in war and as a effect, he also increased the number of senators. He built the Roman Forum and various other buildings like the Temple defended to Jupiter. Furthermore, he besides appropriated Etruscan military accessories for utilise in the Roman military.
 Lucius Tarquinius Priscus, the 5th Male monarch of Rome from 616 BC to 579 BCE, 16th-century depiction published by Guillaume Rouillé;Published by Guillaume Rouille (1518?-1589), Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Lucius Tarquinius Priscus, the 5th Male monarch of Rome from 616 BC to 579 BCE, 16th-century depiction published by Guillaume Rouillé;Published by Guillaume Rouille (1518?-1589), Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Servius Tullius (reigning from 578-535 BC) was the sixth king, and it was he who waged war and won against the Etruscans. He introduced new voting rights for more select groups within Rome and constructed the temple dedicated to the goddess Diana. He was assassinated by his younger daughter, Tullia, and her husband Lucius Tarquinius Superbus, who became the seventh Roman king, reigning from 535-509 BC.
Lucius warred against several cities and was more infamous equally a king, as he was known for beingness aggressive and disrespectful. The King was overthrown subsequently his son raped the daughter of a Roman nobleman, Lucretia, afterwards which she died by suicide. The expulsion of the rex and his family from Rome (due to Lucretia's rape) marked the end of the Roman monarchy.
The Roman Republic (509 BC – 27 BC)
The Roman Republic developed a new governmental system where there were two consuls or magistracies with the senate as the overseeing body of authority. The 2 consuls worked on an annual basis, which meant that 2 new consuls were elected each year.
The consuls had potency within war machine and civilian matters, and were able to object or agree to what the other was doing. This system ensured the prevention of the tyrrany that was commonplace during the Roman monarchy, as this way, the power does not belong to just one person.
The Republican menses saw various civil wars and political upheavals, where Julius Caesar, a Roman general, became dictator with the aim to eventually unify Rome over again. Caesar was assassinated during 44 BC by several senators who felt he was a chance to Rome. Octavius, also known as Augustus, was Caesar's adopted nephew and heir, and information technology was he who eventually started the Roman Empire.
The Roman Empire (27 BC – 476 BC)
The Roman Empire was the get-go of a new period in Rome, and at the atomic number 82 equally the Principate, was Caesar Augustus (otherwise known and built-in equally Gaius Octavius or Octavian). He is remembered as a significant leader in Roman history and ruled during a period that was more peaceful than nearly of Rome's development. This menses is referred to as Pax Romana ("Roman Peace"), and it lasted for almost 200 years.
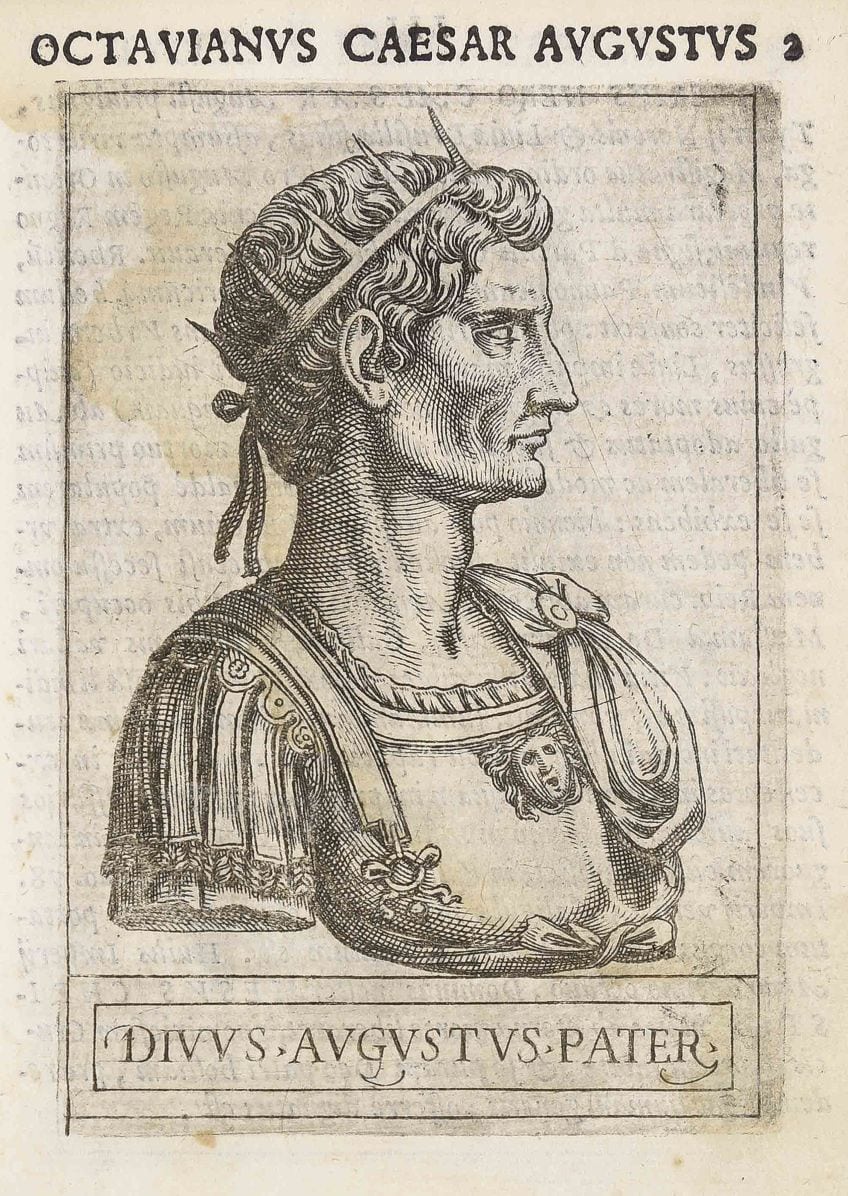 Copper engraving of Octavianus Caesar Augustus by Giovanni Battista de'Cavalieri. The text below reads "Divus Augustus Pater", significant "Male parent Caesar Augustus";Giovanni Battista de'Cavalieri, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
Copper engraving of Octavianus Caesar Augustus by Giovanni Battista de'Cavalieri. The text below reads "Divus Augustus Pater", significant "Male parent Caesar Augustus";Giovanni Battista de'Cavalieri, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
The Autumn of the Roman Empire happened over the years 376 to 476 BC and consisted of the gradual deposition of various political, economic, and social systems. It is a widely debated topic near what events caused the pass up of this keen civilization. What led after the Fall of Rome was the period in Western history referred to every bit the Dark Ages. Information technology is also important to annotation that Rome was divided into the Western and Eastern parts. The Eastern division was ruled by Constantin the Great and known every bit Byzantium, which was later named Constantinople.
Roman Artwork
Ancient Roman art was not completely original in its production; the Romans were influenced by the Etruscans and Greeks before them, as mentioned earlier. The complex interrelations between dissimilar cities, cultures, and countries (Africa, Asia, Europe, and Egypt) makes this a rich area and topic of discussion inside Roman artwork. Beneath, nosotros volition discuss some of the characteristics of Roman Art, specifically Roman Republic art and Roman Empire art.
Roman Paintings
While at that place is not a large collection of ancient Roman paintings, the all-time drove of ancient Roman art came from the remains of Pompeii and Herculaneum. When Mountain Vesuvius erupted in 79 Advertisement, it cached and preserved all sorts of Roman artwork including magnificent murals (wall paintings) painted to decorate the interiors. The murals were largely done as frescoes.
The German archaeologist, August Mau, started excavating the Pompeii remains during the 1800s and developed 4 classifications for the various styles of wall paintings establish. It is also worth noting that these styles occurred in other parts of Rome. Let united states discuss them briefly below.
First Mode: Incrustation Mode
The Incrustation Style developed from around 200 to eighty BCE and is believed to have derived from Hellenistic culture. This style was also called the Masonry Style. It depicted mostly rectangular or brick-like shapes of pigment that appeared similar marble. Information technology was painted in bright colors similar xanthous or red, connected with stucco in-between, which also gave information technology a raised appearance. Examples depicting this fashion can be found in two houses in Pompeii, namely, the House of the Faun and the House of Sallust.
 Frescoes in the first style, from the Casa di Sallustio ('House of Sallust') in Pompei; August Mau (?), died 1909, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Frescoes in the first style, from the Casa di Sallustio ('House of Sallust') in Pompei; August Mau (?), died 1909, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Second Manner: Architectural Style
The Architectural Style occurred around eighty BCE to 100 CE. This style still utilized the imitation of marble blocks, however, in that location was an increment of illusionistic detail using architectural elements (creating illusionistic detail is referred to every bit trompe-l'oeilI). Paintings would appear three-dimensional with some areas actualization real, simply not. Some walls also had life-sized figures depicted on them, which enhanced the sense of realism and three-dimensionality. Examples of this style are seen in the fresco in the sleeping accommodation of Villa of P. Fannius Synistor (50-40 BCE) and the Dionysiac Frieze (dated prior to 79 CE) from the Villa of Mysteries.
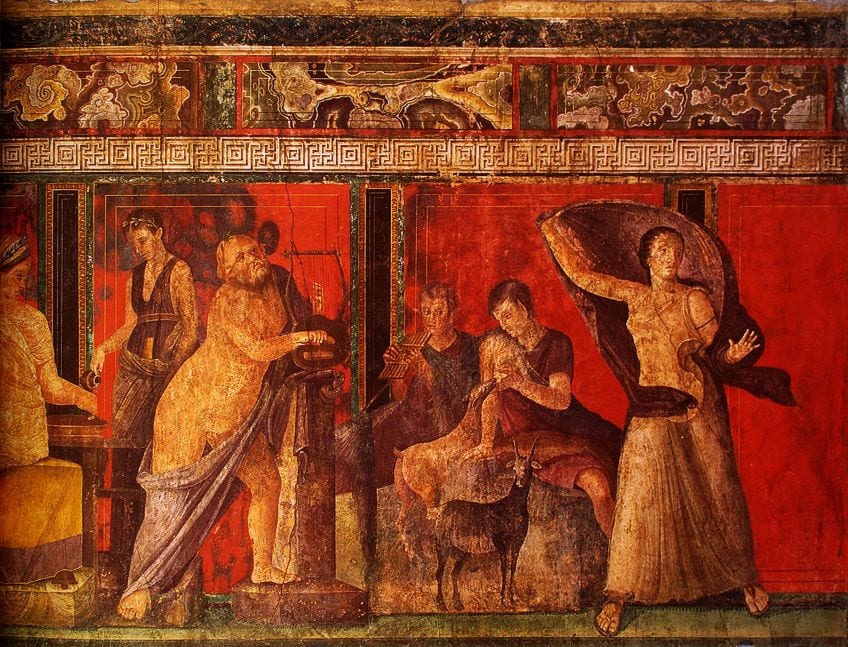 Frieze depicting Silenus belongings a lyre (left), demigod Pan and a nymph sitting on a rock and nursing a caprine animal (center), and a woman with a coat (correct). Fresco from the Villa of the Mysteries, Pompeii, Italia;Unknown writer Unknown author, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Frieze depicting Silenus belongings a lyre (left), demigod Pan and a nymph sitting on a rock and nursing a caprine animal (center), and a woman with a coat (correct). Fresco from the Villa of the Mysteries, Pompeii, Italia;Unknown writer Unknown author, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Tertiary Style: Ornate Manner
The Ornate Style occurred around x BCE to 50 CE. This mode likewise depicted similar architectural elements from the Second Way, simply paintings depicted more than decorative motifs often with monochromatic colors (reds or blacks), which made information technology appear flatter rather than three-dimensional. The unlike motifs utilized took inspiration from florals and the natural environment. They besides depicted images and scenes from Arab republic of egypt. Examples of this style are seen in the Villa Agrippa Postumus (c. ten BC).
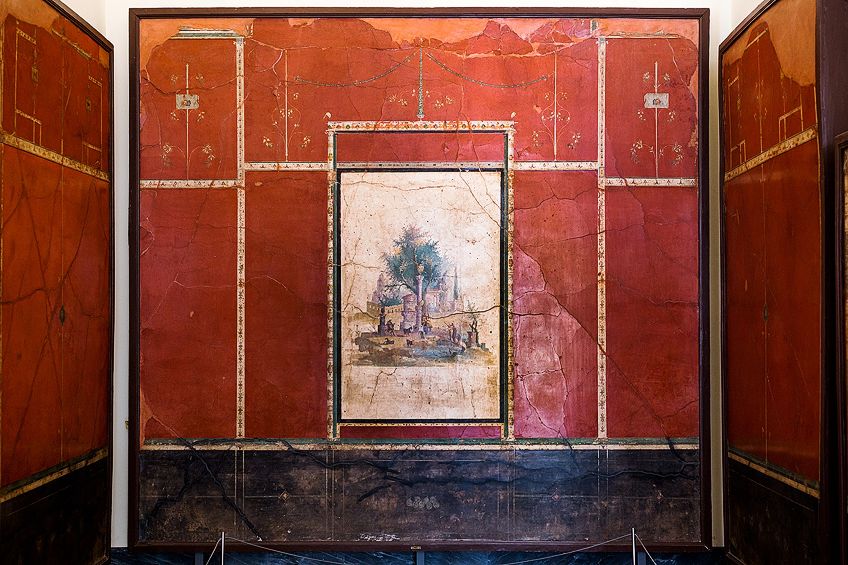 Fresco of human figures and animals in an idyllic rural landscape with sacral buildings and statues, from the third style of Pompeian wall painting;ArchaiOptix, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Fresco of human figures and animals in an idyllic rural landscape with sacral buildings and statues, from the third style of Pompeian wall painting;ArchaiOptix, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Quaternary Manner: "Intricate Style"
The Intricate Style occurred from threescore to 79 CE. This way is oftentimes described as existence a combination of the above-mentioned three styles. It depicted the imitation of marble, the architectural details of painting, as well equally the ornamentation of the more decorative 3rd Style. The subject matter also became more diverse, depicting not only natural scenes of the landscapes, just also mythological themes and figures, as well as the inclusion of nevertheless lives.
An instance of this style is seen in the House of the Vettii, which was a big townhouse with numerous detailed aboriginal Roman paintings decorating the walls in each room. A famous case is in the Ixion Room, featuring multiple panels of various figures and architectural details that brand each console appear as if it is part of the real environment.
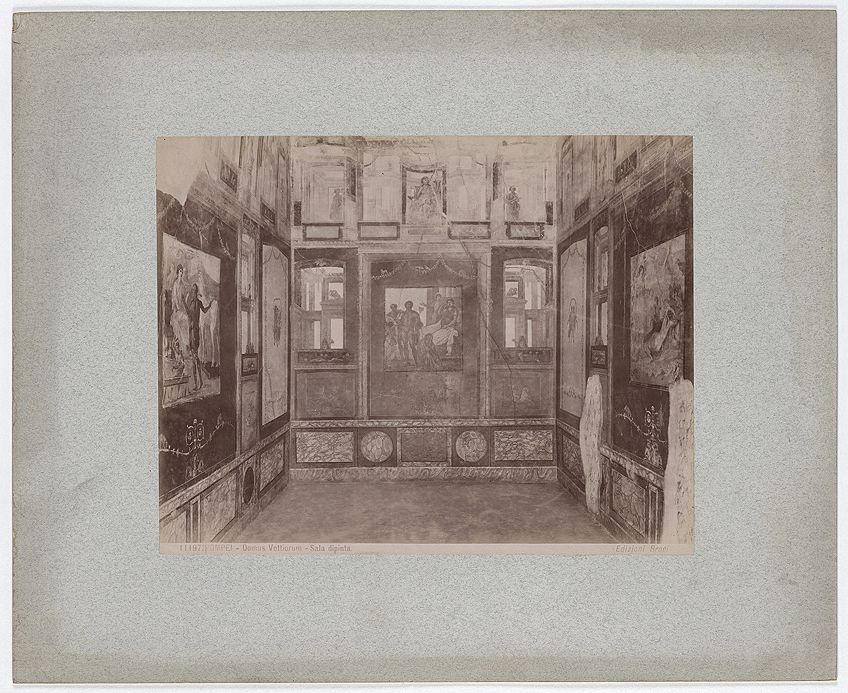 Ixion Room in the Business firm of Vettii, painted in the fourth style past Giacomo Brogi;Giacomo Brogi, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Ixion Room in the Business firm of Vettii, painted in the fourth style past Giacomo Brogi;Giacomo Brogi, CC BY-SA 4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Roman Architecture
When thinking of Roman architecture in that location is commonly i edifice that stands out, one nosotros are all familiar with and, one that is truly eternalized in epic films and literature: the Colosseum. Notwithstanding, this is non the only prominent piece of architecture designed past the Romans.
In fact, Roman compages introduced new and innovative designs and building materials that would shape the hereafter of architecture for centuries to come.
The Romans constructed various types of buildings ranging from temples to buildings suited for entertainment purposes, similar the famous Colosseum, in the shape of an amphitheater. Houses ranged from farmhouses (villas) to apartment blocks (insulae) in more populated urban areas (much like our 21st Century urban living way). The Romans also innovated the building of baths and aqueducts, which allowed clean water into the urban center.
The Roman Architectural Revolution
The Roman Architectural Revolution occurred as a result of the of import discoveries made in using building materials like physical, effectually and between the anest Century BC to threerd Century BC. What is referred to as "Roman physical", or opus caementicium, was fabricated from a new building fabric chosen "pozzolana" (volcanic ash). This was added to the mortar already used past the Romans to make information technology stronger, with the power to fix underwater.
This revolution was as well referred to as the "Concrete Revolution" and enabled more effective systems for using the arch, leading to edifice developments in the vault and dome edifice shapes. A notable example of this was the Groin Vault, adult by the Romans. This consisted of two Barrel Vaults (Barrel Vaults are in the basic shape of a domed arch) joining or intersecting at two right angles.
The Roman architect Vitruvius is also worth noting and knowing in Roman architectural history. Vitruvius was an architect, engineer, and author of the seminal work called De Architectura ("On Compages", c. 30-15 BCE). This text (equally much theoretical every bit it was applied) was dedicated to Emperor Augustus and explored Vitruvius' observations about the nature of compages also as its history.
 De Architectura by Vitruvius, first English translation, based on the French translation past Claude Perrault, printed by Abel Swall and T. Child, 1692; Georges Jansoone (JoJan), Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
De Architectura by Vitruvius, first English translation, based on the French translation past Claude Perrault, printed by Abel Swall and T. Child, 1692; Georges Jansoone (JoJan), Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Republican Roman Architecture
Some examples from the Republican Flow in Roman compages include the Temple of Jupiter Optimus Maximus(c. 150 BC). This was ane of the first architectural constructions in Rome and would influence many other structures due to its blueprint and layout. Its completion engagement was around 509 BCE, the aforementioned time at which the Republican period began and the monarchy came to an stop.
Located on Capitoline Colina, this temple is situated on a podium (giving it considerable height). The porch's (pronaos) depth spans 3 columns with six columns at the frontal edge of the porch, which also offers the only archway into the building. The interior of the temple is divided into 3 rooms (cellae) – this type of layout is referred to as "tripartite" due to the iii-way carve up.
 Temple of Jupiter Optimus Maximus(c. 150 BC);Rijksmuseum, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
Temple of Jupiter Optimus Maximus(c. 150 BC);Rijksmuseum, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
Architecture during this period was influenced by the type of architectural structures from the Etruscan period, equally well as the Greek period. An influential example from the Etruscan catamenia includes the Temple of Minerva (c. 510 BC). Here, we discover the deep-set porch with columns leading into the temple structure.
Other examples from the Roman Republican period include the Sanctuary of Fortuna Primigenia (c. late 2nd Century) located in the now-modern Palestrina (Praeneste is the proper noun of the ancient city). The big circuitous is divided into two structures, the one upper and the other lower. The upper section is role of a hillside with various other structures, including the temple.
 Reconstruction of the Temple of Fortuna Primigenia at Palestrina past Pietro da Cortona;Pietro da Cortona, Public domain, via Wikimedia Eatables
Reconstruction of the Temple of Fortuna Primigenia at Palestrina past Pietro da Cortona;Pietro da Cortona, Public domain, via Wikimedia Eatables
The Temple of Portunus (c. 120-80 BCE) is another example. This is a temple in a rectangular shape, located in Rome almost the master harbor area almost the Forum Boarium. Here, we see the deep-set front porch once more, with two columns in-depth, and four columns lining the front end edge of the porch. The columns are in the Ionic Order style. Along the outer sides of the temple, there are five columns and another 4 along the back end of the temple (the aforementioned as the front side).
Architectural structures, especially temples, were usually constructed every bit monumental offerings, especially in the Forum Boarium where in that location would accept been more people and events due to its location near the harbor. This temple was believed to be dedicated to Portunus, a Roman god of harbors, gates (keys), and livestock.
Imperial Roman Architecture
Imperial Roman architecture experimented more with newly found building materials like concrete. It was used not just for structural purposes but besides artful purposes, which is evident in the vaulted arches of the Markets of Trajan (106-12 CE).
The Markets of Trajan was a part of the Forum of Trajan, dedicated to the emperor Trajan. This was besides the last Roman forum built equally part of the Roman fora (the plural word for forum). Forums were large structures for public gatherings and rituals. This one was designed by the architect Apollodorus of Damascus.
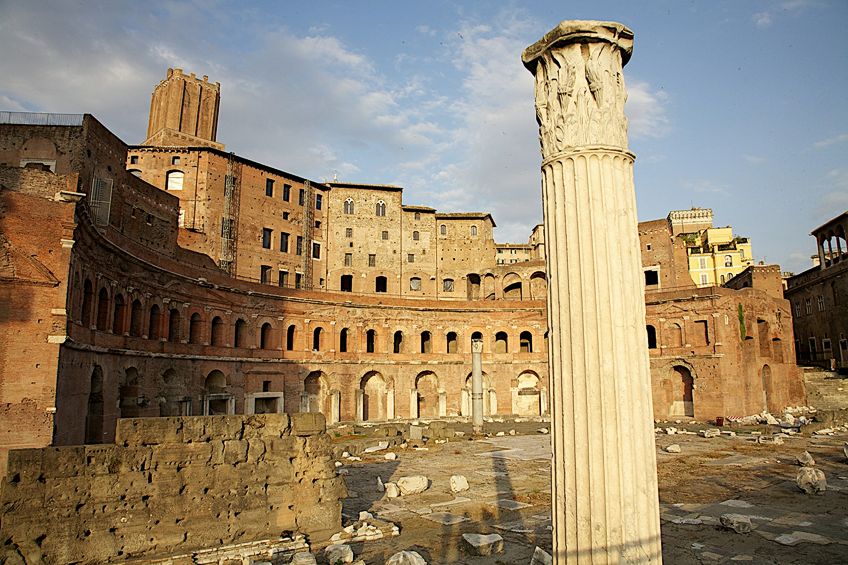 Forum of Trajan in Rome;Jan Hazevoet, CC BY 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Forum of Trajan in Rome;Jan Hazevoet, CC BY 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
The Colosseum (72-eighty CE) is among the most famous Roman architectural creations. Its location is in the centre of the city of Rome. Construction was started past the Roman Emperor Vespasian and concluded with his son, Titus. It was originally chosen the Flavian Amphitheater (due to the emperors beingness of Flavian descent).
The Colosseum is an elaborate construction of architectural design and was built for the Romans as a gift. Some of the chief activities that took place were gladiatorial games and brute fight shows. It was able to seat over 50 000 attendees and measures 620 10 513 feet. There are 80 entrances designed as archways, each with an inscription of its number. The columns supporting the arches combine all three Classical Order styles (Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian).
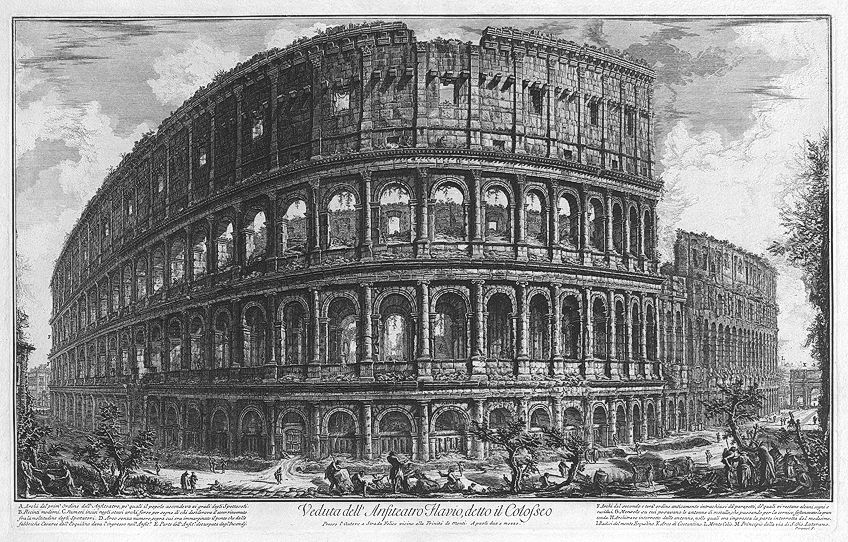 A cartoon of the Colosseum by Giovanni Battista Piranesi, 1757; Giovanni Battista Piranesi, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
A cartoon of the Colosseum by Giovanni Battista Piranesi, 1757; Giovanni Battista Piranesi, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Some other architectural construction, the Arch of Titus (c. 81 CE) was congenital to award the emperor Titus and the victory over the Jewish-Roman war. The arch is located in Via Sacra in Rome and is 50-feet-high and 44-anxiety-wide. It depicts elaborate and decorative relief sculptures of the events of the Jewish-Roman war, in which Vespasian and Titus fought together. The arch too has columns in fluted and unfluted styles, and information technology was this curvation that acted as inspiration for the pattern of the Arc de Triomphe (1806) in Paris.
The Pantheon (113-125 CE) is another monumental case of the innovations made in Roman architecture. This temple, or "dynastic sanctuary", was commissioned by Marcus Agrippa in accolade of Augustus. However, due to damage from fires in 110 CE, Emperor Trajan set up out to rebuild it, simply after his demise, Emperor Hadrian rebuilt information technology.
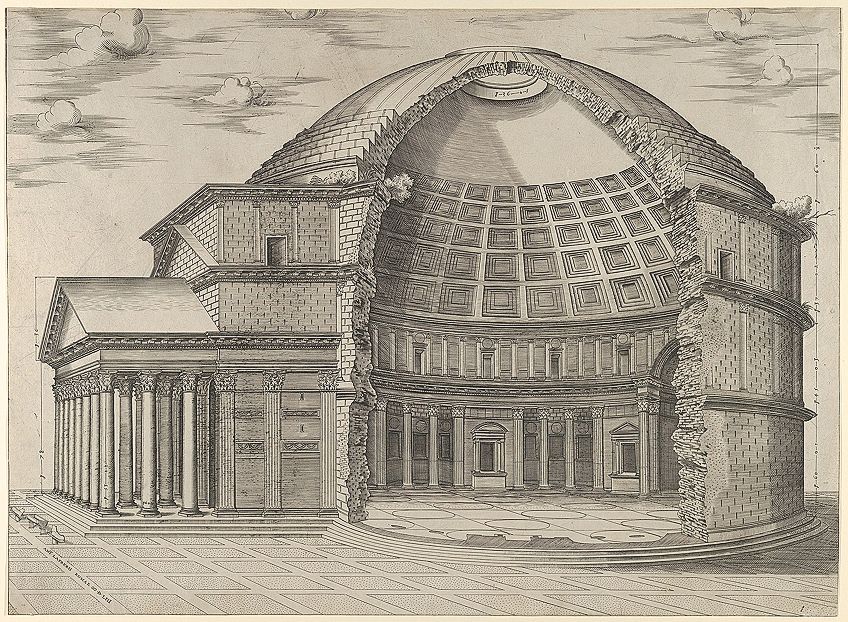 Engraving of the Pantheon in Rome, seen from the side, cutting away to reveal the interior, 1553;Metropolitan Museum of Art, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
Engraving of the Pantheon in Rome, seen from the side, cutting away to reveal the interior, 1553;Metropolitan Museum of Art, CC0, via Wikimedia Commons
The design of the Pantheon depicts a large, rounded structure with a rectangular front or portico. The portico has eight Corinthian-way columns along its edge and two sets of four columns that bridge its inner width to the archway. The dome measures 142 feet in diameter and is made from concrete.
Inside the rotunda (the rounded role of the edifice) of the Pantheon, there is an oculus at the top tip of its dome (this was the only source of calorie-free to enter the building, forth with the archway) surrounded by coffered designs gear up in 28 divisions all the style around. Furthermore, what made this construction more unique was the use of unreinforced concrete.
Roman Sculpture
Roman sculpture was various in its range and typically done in marble or statuary. Many Roman sculptures were frequently depictions inspired past Etruscan and Greek sculptures. It was ofttimes believed the Romans copied these cultures and left no innovative originals of their own. Additionally, at that place was a demand for sculptures, which further drove the Romans to mass-produce.
This is a debated topic, but information technology should be noted that the Romans contributed more in terms of originality than might be believed.
Of the primary forms of Roman sculpture was portraiture. These were popular busts of of import figures of the time, be information technology leaders or political figures. Many people would place these busts in the entrances of buildings for the public to run across them. A characteristic trait among these portrait busts was the delineation of realism in the effigy. Some would appear with all their "imperfections", similar scarring or wrinkles.
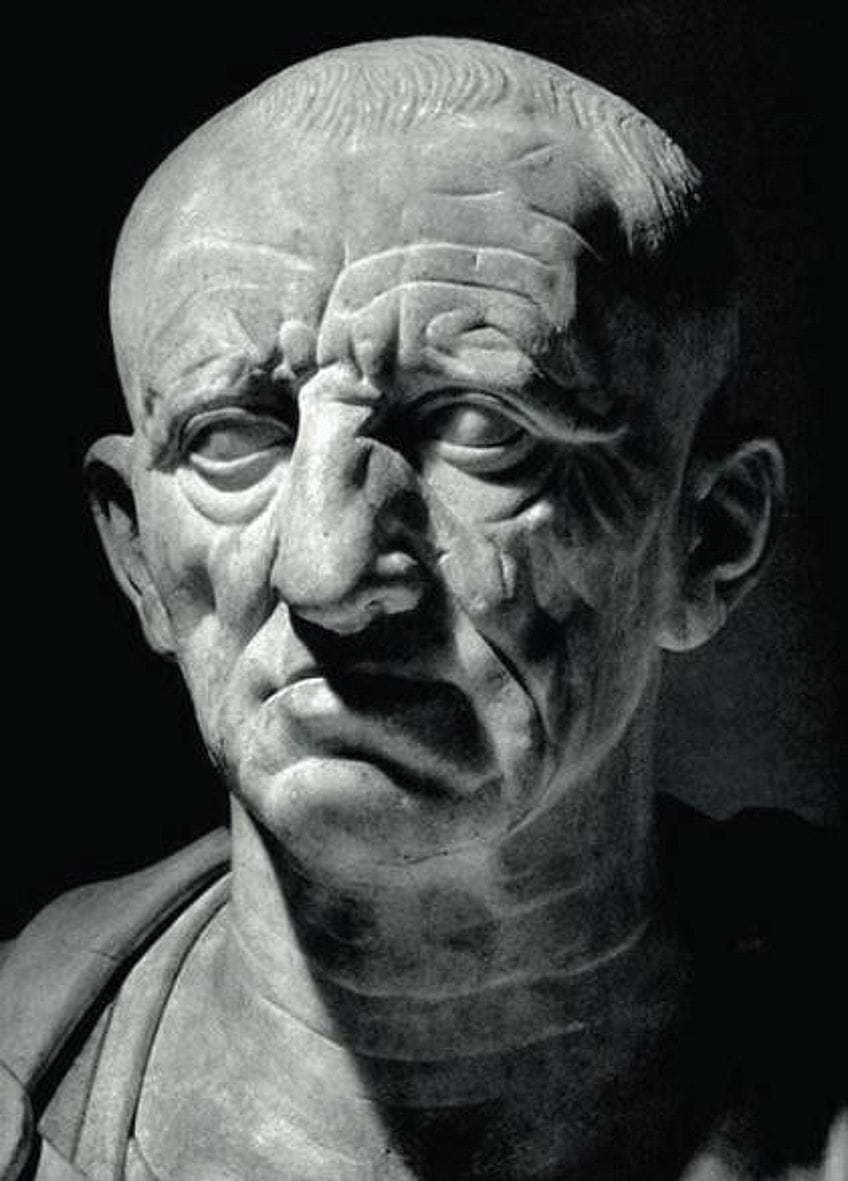 Patrizio Torlonia, or Caput of a Roman Patrician(1st Century BCE);Unknown author Unknown author, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
Patrizio Torlonia, or Caput of a Roman Patrician(1st Century BCE);Unknown author Unknown author, Public domain, via Wikimedia Commons
This realism in figures is referred to as "verism", which is a stylistic departure compared to the Greek style of portraying the heroic and warrior-like masculine figures. The Roman style became more "warts-and-all". There is likewise scholarly argue most the significant of why these portraits were portrayed in such realistic manners.
Some theories suggest that these "imperfections" reflected personality traits like wisdom or beauty. This style became more prevalent during the Republican catamenia and throughout the Majestic period.
Portraits were normally of men more than women, although at that place were some portraits of women. Examples of pop Roman busts include the Head of a Roman Patrician (anest Century BCE) and the Fonseca Bust (twond Century BCE), which is a more idealized depiction of a woman to indicate qualities of beauty and feminine fairness.
Augustus of Prima Porta (onest Century BCE) is another popular marble sculpture depicting Augustus himself. In this sculpture, we see the tendency towards a more idealized depiction of the emperor that alludes to the Classicism nosotros see from the Greeks.
 Sculpture of Emperor Augusto, located in Prima Porta, Rome, discovered in 1863;Michal Osmenda from Brussels, Belgium, CC BY-SA ii.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Sculpture of Emperor Augusto, located in Prima Porta, Rome, discovered in 1863;Michal Osmenda from Brussels, Belgium, CC BY-SA ii.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Reliefs were some other popular class of sculpture amongst the Romans, with strong historical subject thing about state of war, conquests, and diverse other aspects relating to the life and events of the emperor. The functions of these relief sculptures were celebratory or educational (didactic).
Although the Romans depicted and revered their Roman gods, their sculptures became more different in subject matter than the predominant mythological subject matter widely depicted in Greek Art. A popular case of Roman relief sculpture is Trajan'due south Column (c. 110 CE) and the Column of Marcus Aurelius (c. 180-193 CE).
Trajan's Column is a awe-inspiring example of what the Romans achieved in terms of relief sculpture. It was commissioned by Emperor Trajan in 107 CE in celebration of his victory over Dacia (including two conquests). Information technology is located in Trajan'south Forum in Rome. Information technology measures 125-anxiety-tall and appears every bit a spiral narrative in a low-relief technique around the column in the Doric Order way.
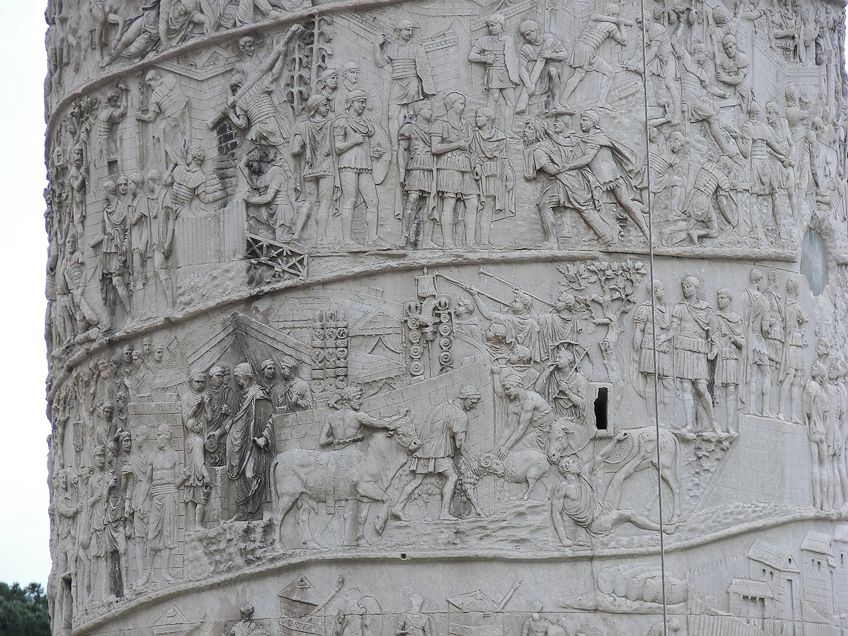 Reliefs on the Columna Traiana (Trajan'southward Column, c. 110 CE) in Rome;Wknight94, CC BY-SA iii.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Reliefs on the Columna Traiana (Trajan'southward Column, c. 110 CE) in Rome;Wknight94, CC BY-SA iii.0, via Wikimedia Commons
When nosotros await at the Column of Marcus Aurelius, it is nearly on par with Trajan'due south Column in its monumental qualities. It was also inspired past the sometime column. However, information technology is different in its sculptural manner, using the high-relief technique. This created a more dramatic and expressive effect as the figures were more raised from the surface of the cavalcade.
The figures' heads were often done larger than was naturally proportional and viewed from the frontal plane. The diverse techniques used to depict figures forth the spiral relief effectually the column created more perspective and depth.
Marcus Aurelius' column was in commemoration of his two military campaigns in the Danube against the Quadi and Marcomanni. It stands at 100-feet-tall (in Roman anxiety) and is in the Doric Order manner. The column is located in the Piazza Colonna in Rome.
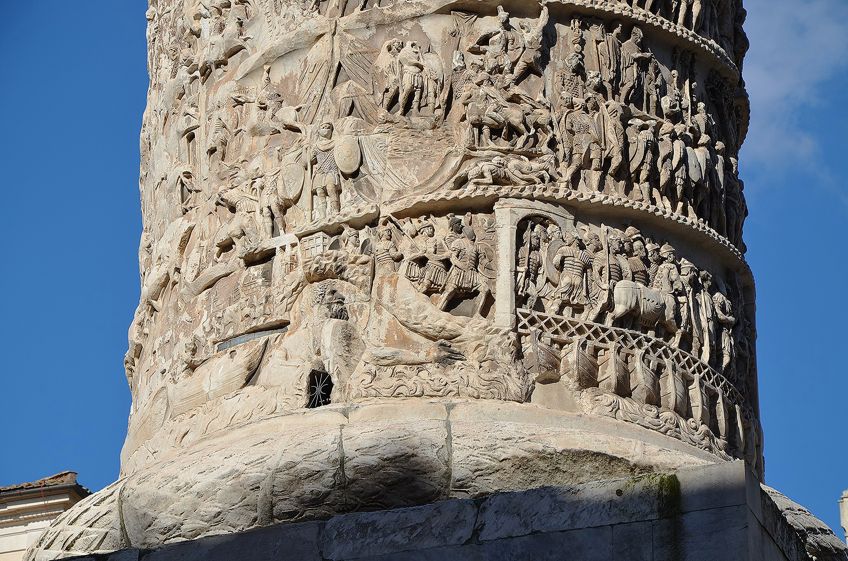 Detail of the Cavalcade of Marcus Aurelius, Rome; Carole Raddato from FRANKFURT, Germany, CC Past-SA 2.0, via Wikimedia Eatables
Detail of the Cavalcade of Marcus Aurelius, Rome; Carole Raddato from FRANKFURT, Germany, CC Past-SA 2.0, via Wikimedia Eatables
Other examples of Roman sculptures include the Equestrian Statue of Marcus Aurelius (c. 163-173 E), which is made of bronze and depicts Emperor Marcus Aurelius on his horse, raising his right arm while his equus caballus raises his right front leg. The statue is only one example displaying the importance placed on Roman leaders and their horses because it showcased military status and achievement (these are otherwise referred to as Equestrian sculptures).
The Portrait of the Four Tetrarchs (c. 300 CE) is an example of a sculpture made during the Late Roman Empire. It is located on the corner of St. Marker'due south Basilica in Venice. It was made from a rock called porphyry and is majestic-red in color. This stone was besides associated with the power of dignity in the Roman Empire; the color purple was associated with nobility or royalty (the Greek word porphyra means "majestic" in English language).
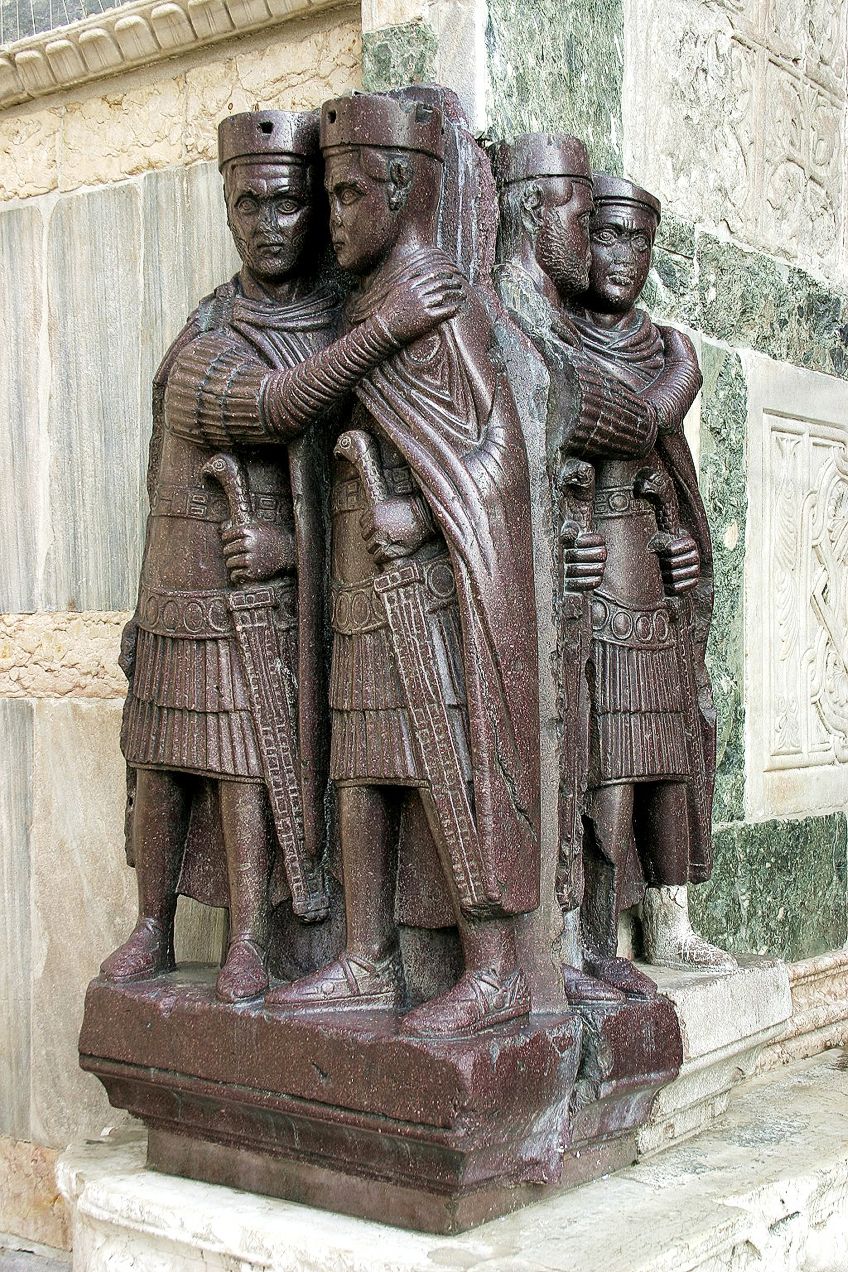 The tetrarchs (from the Greek words for "Four rules") were the four co-rulers that governed the Roman Empire as long equally Diocletian's reform lasted. Here they were portrayed embracing, in sign of harmony, in a porphyry sculpture dating from the 4th century, produced in Asia Minor, today on a corner of Saint Mark'southward in Venice;Nino Barbieri (talk · contribs), CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
The tetrarchs (from the Greek words for "Four rules") were the four co-rulers that governed the Roman Empire as long equally Diocletian's reform lasted. Here they were portrayed embracing, in sign of harmony, in a porphyry sculpture dating from the 4th century, produced in Asia Minor, today on a corner of Saint Mark'southward in Venice;Nino Barbieri (talk · contribs), CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
This statue depicts the Four Tetrarchs assigned by Emperor Diocletian to mitigate the pressure of ruling an Empire as a sole emperor (there are two augusti and two caesares). In this sculpture, we notice the iv figures in two groups of the older, senior emperors (augusti) and the younger, junior, emperors (caesares). They are all holding their swords with one mitt and placing their arm on the other next to them as a sign of camaraderie.
What is different near this sculpture is the motion abroad from the realism nosotros see in many of the Roman Empire art sculptures. The Four Tetrarchs are depicted subjectively. In other words, their anatomical symmetry and facial expressions, or lack thereof, are not in proportion equally we have seen in other examples like Augustus of Prima Porta (1stCentury BCE).
The Weakened Westward Remains Eternal
The Western Roman Empire came to an end considering of various socio-political and ecology factors. In turn, the Eastern Empire remained potent. Emperor Constantine created a renewed Roman capital letter known as Byzantium (later renamed Constantinople). Roman Art was somewhen influenced past the Due east, which adult into what we know today as Byzantine Art (this likewise ushered in early on Christian Art).
Roman Art was indeed an era of innovation and discoveries of a civilization seeking advancement of self and life, contrary to them also being known every bit "copying" the Etruscans and Greeks.
Alee of their time, the Romans introduced new means of doing things. Not but did they pioneer architectural structures that would after exist emulated by many other architects and artists during the Renaissance period, merely they were also a civilization for the progression of their people and portraying them and their history every bit celebrations and commemorations.
Ofttimes Asked Questions
What Is Roman Art?
Roman art has a long history that dates back all the manner to the time of the Etruscans, the Roman Kingdom, the Roman Republic, and the Roman Empire. Roman art spans beyond different artistic media, namely wall paintings (frescoes), sculptures, architecture, mosaics, jewelry, various ornaments and accessories made from drinking glass and silverware, amongst many others.
What Are the Characteristics of Roman Art?
When it came to Roman paintings, the main characteristics included landscapes and still lives as discipline matter incorporated into wall paintings and murals alongside various other figures and animals. Roman paintings were also done as frescoes (wet paint on wet plaster). The Romans too invented the Roman Groin Vault in architecture, which enhanced the older Mail service-and-Lintel systems used by the Greeks.
What Are the Iv Styles of Roman Painting?
Nearly of the Roman paintings we see today are from examples excavated from Pompeii and Herculaneum, preserved nether the ashes of the Mountain Vesuvius eruption in 79 Advertizing. The German archaeologist, August Mau, excavated the Pompeii remains during the 1800s and developed four classifications for the styles of wall paintings found, namely, Incrustation Mode, Architectural Style, Ornate Style, and Intricate Style.
What Was the Difference Between Greek and Roman Fine art?
What set the Romans apart from the Greek style of art, specifically sculpture, was their inclination to depict their bailiwick matter more than realistically. This realism contrasted with the idealized figures portrayed in Greek sculptures. The Romans depicted their figures (mostly men) with all their "imperfections" similar old age, wrinkles, or scars to point personality traits similar wisdom. Women were non depicted often, but they would announced fairer with fewer "warts-and-all" to represent the ideals of beauty and stylish styles of the time.
Did the Romans Invent Concrete?
The Romans innovated the employ of concrete, which led to more innovative building designs like the Groin Vault and the dome structures. This started the "Roman Architectural Revolution" or the "Physical Revolution".
Source: https://artincontext.org/roman-art/
0 Response to "What Is Ancient Roman Art What Is Middle Ages Art"
Post a Comment